The Potential of IoT: Shaping the Future of Connectivity.
The Future of IoT How Does IoT Work? Who invented IoT? Current State of IoT?

The Internet of Things (IoT) redefines the way we interact with the world around us. At its core, IoT represents a network of interconnected devices, enabling them to communicate, collect, and exchange data seamlessly.
In the ever-evolving landscape of technology, the Internet of Things (IoT) has emerged as a groundbreaking concept that is reshaping the way we live, work, and interact with the world around us. IoT is a network of interconnected devices that communicate and share data with each other over the internet, creating a seamless web of information and automation. From smart homes to industrial machinery, IoT’s impact is general, promising a future where connectivity transcends boundaries and transforms our daily experiences. In this blog, we will delve into the essence of IoT, its current state, and the exciting future it holds.
Understanding IoT
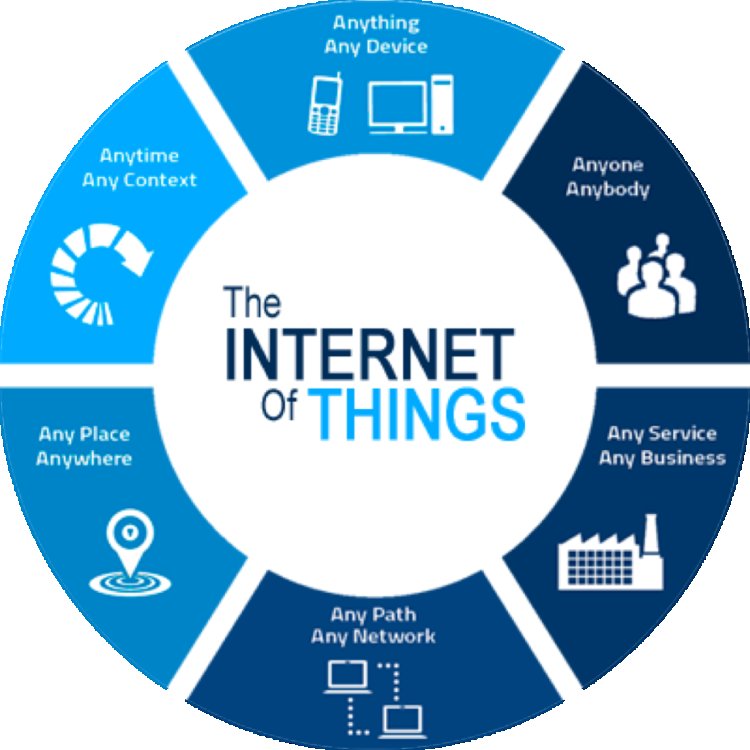
IoT revolves around the idea of driving in everyday objects with sensors, software, and connectivity, facilitating data exchange and automated actions. These devices, ranging from household appliances and wearable gadgets to vehicles and infrastructure systems, gather valuable information and utilize it to streamline processes, enhance efficiency, and improve overall functionality.
The fundamental principle of IoT lies in its ability to create a web of interconnectedness, allowing devices to communicate and collaborate autonomously, often without human intervention. For instance, a smart thermostat can adjust the temperature based on occupancy patterns, while wearable health trackers monitor vital signs and provide real-time feedback for individuals.
Who invented IoT?
The term 'Internet of Things' was coined in 1999 by the computer scientist Kevin Ashton. While working at Procter & Gamble, Ashton proposed putting radio-frequency identification (RFID) chips on products to track them through a supply chain. The idea was often called “embedded internet” or “pervasive computing”. But the actual term “Internet of Things” was coined by Kevin Ashton in 1999 during his work at Procter & Gamble.
The first IoT device was a toaster invented by John Romkey in 1990.
Current State of IoT:
As of now, IoT has already made a significant impact across various industries. In the realm of healthcare, IoT devices monitor patients' vital signs, providing real-time data to healthcare professionals for better diagnosis and treatment. In smart cities, IoT is used to manage traffic flow, monitor environmental conditions, and enhance public safety. The industrial sector has embraced IoT for predictive maintenance, optimizing production processes, and improving overall efficiency.
How Does IoT Work?
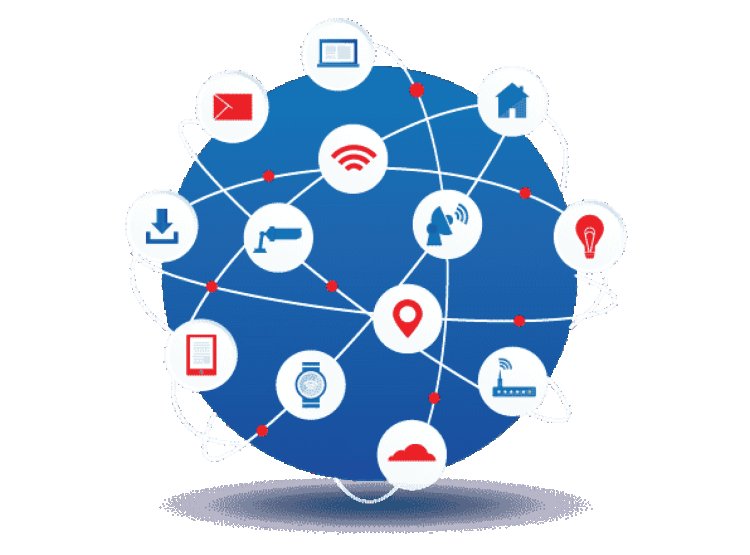
IoT operates through a simple yet intricate process. Devices equipped with sensors gather data from their surroundings. This data is then transmitted over a network (often the internet) to a centralized system or cloud platform, where it's analyzed and utilized for various purposes. For instance, a smart thermostat collects temperature data, transmits it to a cloud server, and adjusts the room temperature based on preset preferences.
Applications of IoT
The applications of IoT are virtually limitless. In homes, smart devices like thermostats, security cameras, and voice assistants enhance convenience and efficiency. In healthcare, IoT devices monitor vital signs, track medication adherence, and enable remote consultations. Industries leverage IoT for predictive maintenance, inventory management, and optimizing operations.
Transformative Applications
IoT’s impact spans across various domains, revolutionizing industries and enhance our lives:
- Healthcare: Remote patient monitoring, wearable devices, and smart medical equipment enable personalized healthcare, improving treatment outcomes and patient experiences.
- Smart Cities: IoT-driven solutions optimize resource management, traffic flow, and public services, fostering sustainable and efficient urban environments.
- Industrial IoT (IIoT): Factories leverage IoT for predictive maintenance, optimizing production processes, and ensuring operational efficiency.
- Agriculture: IoT sensors and data analytics assist farmers in precision agriculture, optimizing crop yields, and resource utilization.
The Future of IoT:
The future of IoT promises even more transformative changes, as technology continues to advance and the ecosystem expands. Here are some key trends and developments shaping the future of IoT:
- 5G Connectivity: The rollout of 5G networks will revolutionize IoT by providing faster and more reliable connectivity. This will enable quick communication between devices, surfacing the way for new applications and services.
- Edge Computing: Edge computing involves processing data closer to the source rather than relying on a centralized cloud server. This reduces response time and enhances the efficiency of IoT systems, making them more responsive and capable of handling massive amounts of data.
- Artificial Intelligence (AI) Integration: The integration of AI with IoT will enable devices to analyze and interpret data in real-time, leading to more intelligent decision-making. This combination will fuel advancements in predictive analytics, automation, and personalized user experiences.
- Security Enhancements: As the number of connected devices grows, so does the concern for security. The future of IoT will see increased focus on implementing robust security measures, including encryption, authentication, and secure device management, to protect against cyber threats.
- Expansion in Healthcare and Wellness: IoT will play a pivotal role in the healthcare sector, with the development of wearable devices, remote patient monitoring, and smart healthcare solutions. These innovations will lead to more personalized and efficient healthcare delivery.
- Environmental Monitoring: IoT will contribute to environmental sustainability by facilitating better monitoring of pollution levels, climate conditions, and resource utilization. This data can be utilized to make informed decisions and implement measures for a greener future.
Challenges and Opportunities
While IoT holds immense promise, it also poses challenges, including privacy concerns, interoperability issues, and cybersecurity threats. Addressing these challenges requires collaborative efforts from stakeholders to establish standards, ensure data privacy, and fortify security measures.
However, the opportunities presented by IoT are boundless. As technology continues to advance, the integration of IoT into various facets of our lives will unlock new possibilities, transforming industries, enhancing productivity, and fundamentally reshaping the way we interact with the world.

Conclusion:
The Internet of Things is not just a technological evolution; it is an ideal shift that is redefining how we interact with our surroundings. As IoT continues to mature, the fusion of connectivity, data analytics, and artificial intelligence will open up new possibilities across industries and improve the overall quality of life. The future of IoT is bright, promising a world where devices seamlessly collaborate to enhance efficiency, convenience, and sustainability. Embracing this technological wave is not just an option but a necessity as we step into a future that is more interconnected than ever before.
------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
- Contact us: 8888647482
- Email id: sunil@meratemplate.com
- Telegram - https://t.me/sunilyadavtutorial
- Youtube - https://www.youtube.com/c/MeraTemplate
Thank you so much for taking the time to read my article.




 Mera Template
Mera Template